The Arctic is currently experiencing a reversal event causing the polar vortex to spin in the opposite direction.
At the beginning of this month, an unexpected atmospheric warming incident led to the Arctic’s polar vortex changing its course. The circular mass of frigid air is currently rotating in the opposite direction, resulting in an unprecedented surge in ozone levels that may have repercussions on worldwide weather systems.
The recent surprise warming in Earth’s atmosphere has caused a significant reversal event in the polar vortex, resulting in it swirling in the opposite direction. This reversal is considered one of the most extreme atmospheric U-turns witnessed in recent times.
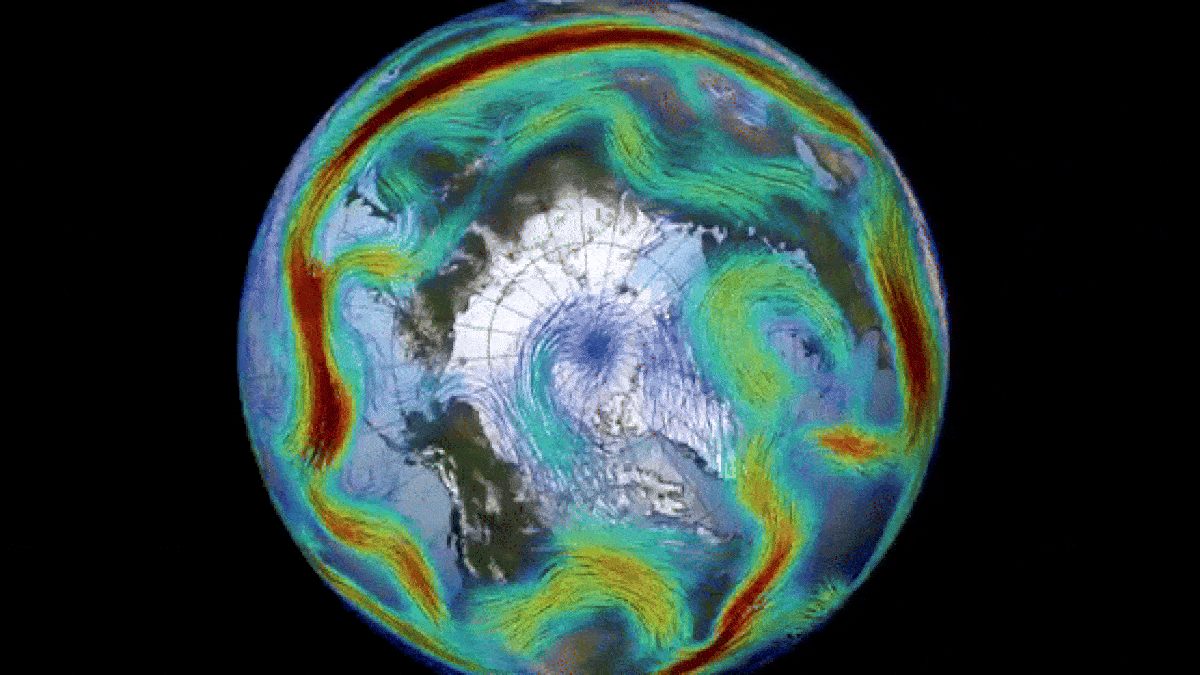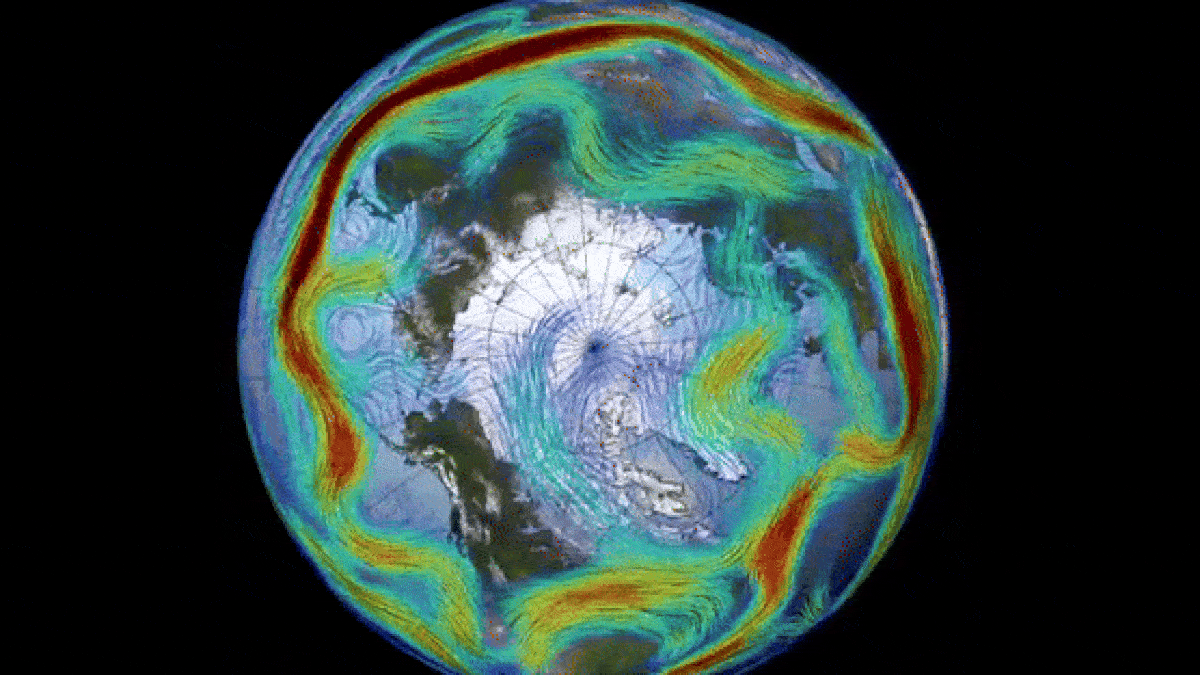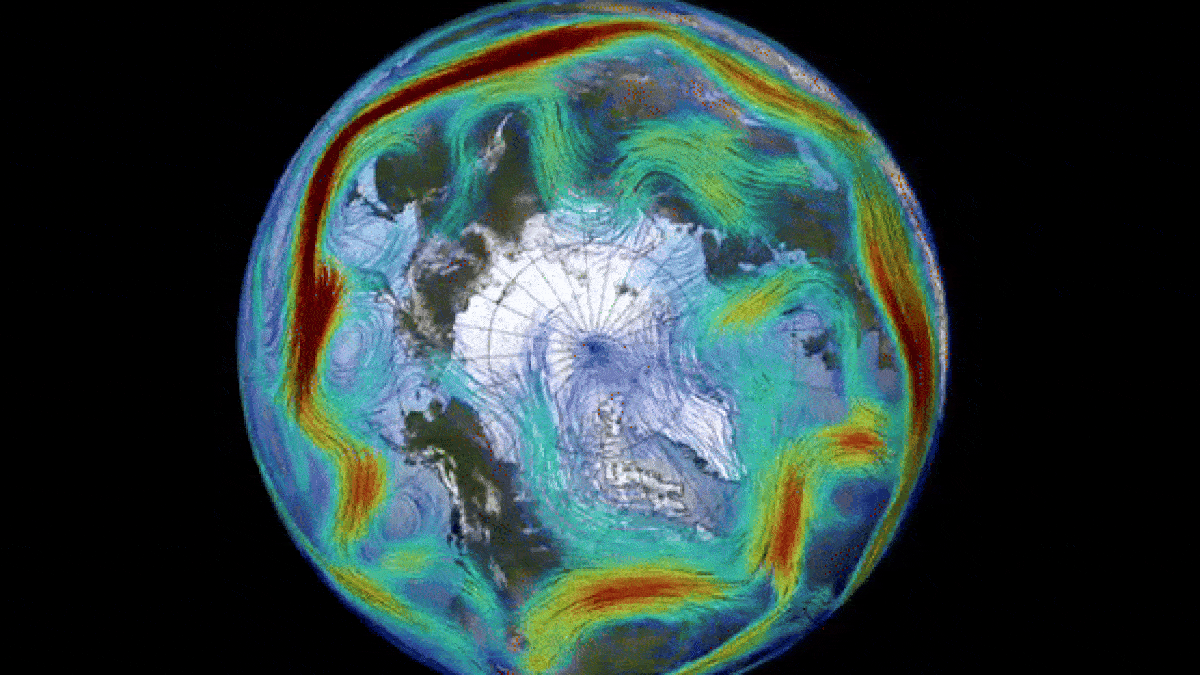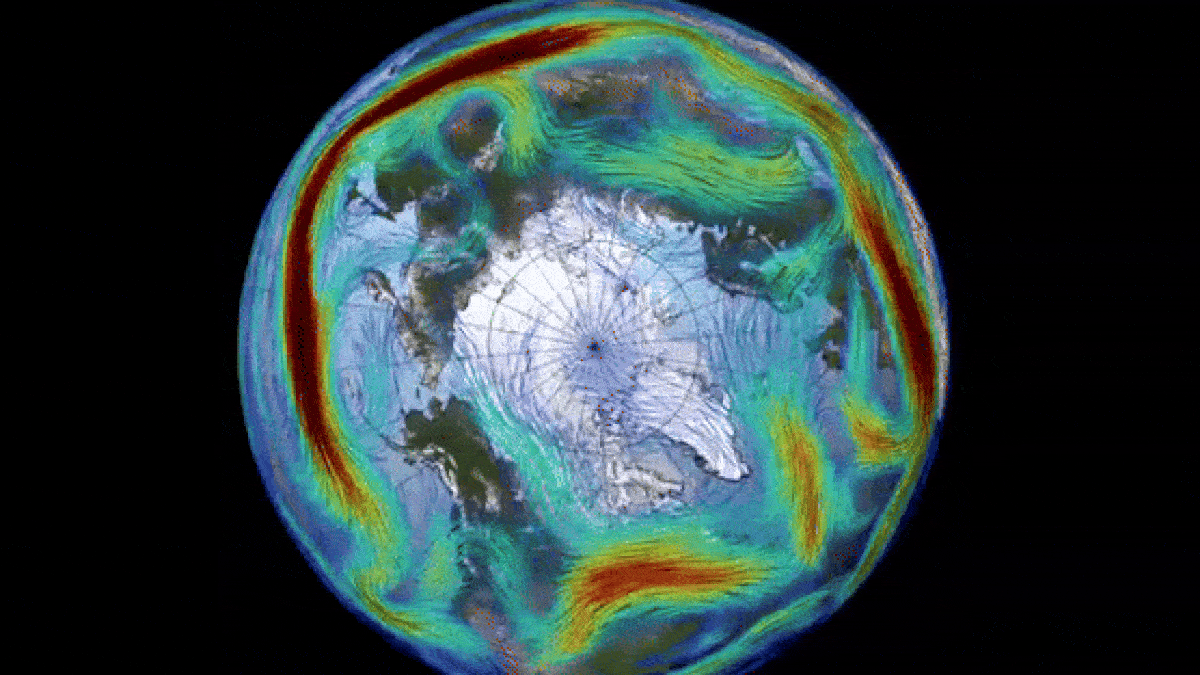
Historically, disruptions in the polar vortex have led to severe cold weather and storms across large areas of the United States. However, the current change in direction is not expected to result in a similar “big freeze.” Nevertheless, this sudden switch has caused a remarkable “ozone spike” above the North Pole.
The polar vortex, which is most prominent during winter months, extends into the stratosphere, the second layer of the atmosphere, reaching up to approximately 30 miles (50 kilometers) above the Earth’s surface. The vortex rotates counterclockwise with wind speeds of around 155 mph (250 km/h), equivalent to the speed of a Category 5 hurricane, as stated by the U.K. Met Office. A similar vortex also encircles Antarctica during the southern winter.
Temporary reversals of polar vortices, known as sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) events, can occur. These events can last for days, weeks, or even months and are triggered by rapid increases in stratospheric temperatures, sometimes reaching up to 90 degrees Fahrenheit (50 degrees Celsius) within a couple of days, according to the Met Office.

According to Spaceweather.com, the ongoing reversal event in the Arctic started on March 4th. Nevertheless, there are signs that the winds are gradually weakening, suggesting that the vortex will soon resume its usual path.
Amy Butler, a climate scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and author of NOAA’s new polar vortex blog, described the recent event as a significant reversal. She mentioned that the speed of the reversed winds ranks this occurrence among the top six on record.
Changes in the polar vortex can have an impact on U.S. weather patterns, as seen in 2019 when a severe cold front swept across the Midwest. These extreme weather events are a result of the polar vortex altering the jet stream, which exposes lower latitudes to frigid Arctic air masses.
Despite the recent disruption, the shape of the jet stream remains unchanged, indicating that weather patterns are likely to stay relatively stable, as reported by Spaceweather.com.
Nevertheless, the shift in Arctic air temperatures has led to the absorption of significant amounts of ozone from lower latitudes, resulting in a temporary ozone spike – the opposite of an ozone hole. Currently, there is a higher concentration of ozone around the Arctic than in any other year on record, according to Spaceweather.com. However, this ozone spike is expected to dissipate once the polar vortex returns to its normal state.
According to Butler’s post on NOAA’s polar vortex blog, the recent reversal is the second one this year, with a previous smaller event occurring in January that led to a brief cold snap in certain states.
Butler also mentioned in the NOAA blog that historical data indicates SSW events are more common during El Niño or La Niña phases, which are part of a natural cycle of global warming and cooling. These phases create more instability in global weather systems, increasing the likelihood of reversal events.
Given the current major El Niño phase we are experiencing, there is a higher probability of additional reversals or disruptions occurring in the next year or so.
Do not forget to share your opinion with us to provide you with the best posts !




0 Comments